What Is Website Crawling? A Complete Guide to Web Crawlers for SEO
- May 27, 2025
- 0

Ever wondered how Google or Bing finds your content and decides where to rank it? Behind the scenes, search engine web crawlers are constantly working, scanning websites across the internet. If you want to rank, you need to understand what is website crawling and how web crawlers work.
This post will break down for you from the basics to the technicals in such a way that’s its easy to digest, even if you’re not super tech-savvy.
Let’s start with the basics: what is website crawling?
Website crawling is the process where search engines send out bots known as web crawlers to discover new and updated content on the web. These bots now browse pages, follow links, and bring data back to the search engine for indexing.
Think it like a librarian scanning new books and organizing them so they’re easy to find later. If your site isn’t being crawled properly, it’s like your book never made it to the shelf.
A website crawler or more technically, a search engine web crawler is a bot used by search engines like Google (Googlebot), Bing (Bingbot), or tools like Ahrefs (AhrefsBot).
To:
So, what is a web crawler in simple terms? It’s a scout, constantly roaming the web, and reporting back what it finds.
All crawlers are not built the same. They aim to gather information, the purpose and functionality of each depends on who’s using them and why.
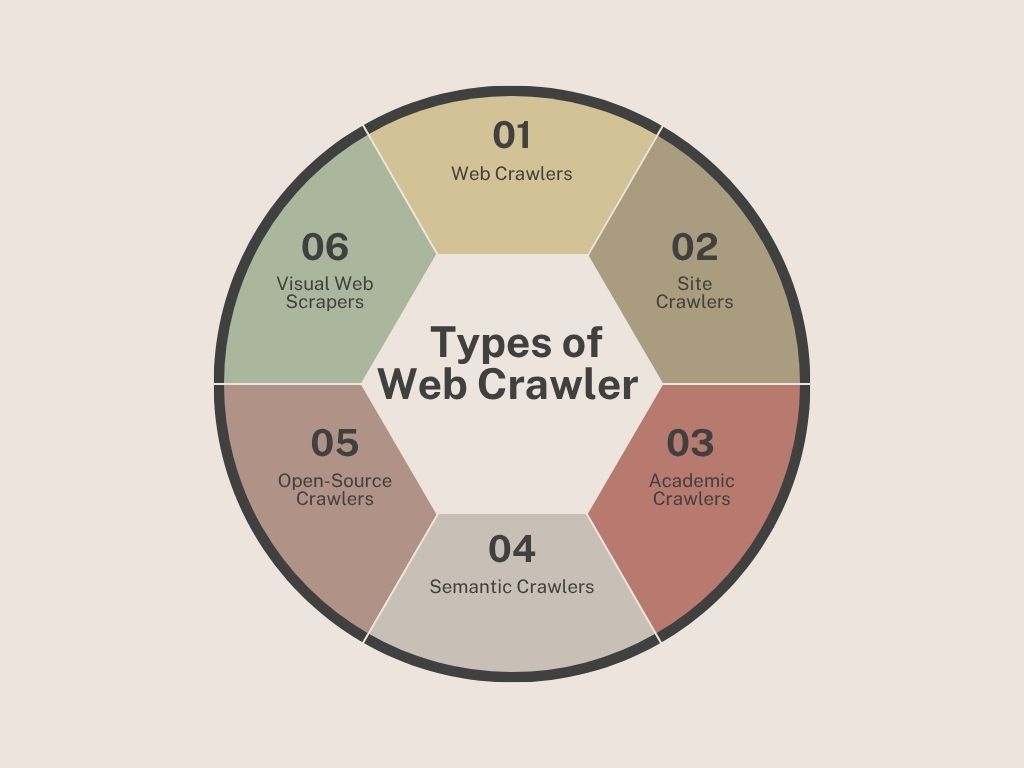
The main types of web crawler you should know are:
The general-purpose bots used by major search engines like Google and Bing.
Goal: To index the entire internet or as much of it as possible.
Examples: Googlebot (used by Google), Bingbot (used by Bing)
Purpose: Crawl billions of web pages to understand what they’re about and determine their ranking in search results. “Big crawlers” that decide whether your site shows up in a Google search or not.
Crawlers built for website owners and SEO professionals. Rather than crawling the whole web, they focus on analyzing a specific site to identify issues that might hurt rankings.
Examples: AhrefsBot (for Site Audit), Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Purpose: Help in auditing your own site, checking for broken links, missing tags, duplicate content, crawl errors, and more.
If you care about your site’s technical health, these are the crawlers you want working for you.
Specialized crawlers that only focus on indexing research papers, journals, and academic content.
Examples: Google Scholar Bot, Semantic Scholar
Purpose: To help students, researchers, and educators find credible academic sources and citations.
Instead of crawling blogs or eCommerce stores, they dig into university libraries and scientific publications.
Semantic crawlers try to understand the meaning behind the content. They use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to detect relationships between ideas and entities.
Examples: Diffbot, custom semantic crawlers for AI training
Purpose: Ideal for structured data extraction and building knowledge graphs.
These bots don’t just read your content it comprehend it.
If you want to build your own crawler then open-source crawlers is for you. These are flexible frameworks that developers can customize for specific needs from scraping job listings to monitoring competitor prices.
Examples: Scrapy (Python-based), Apache Nutch
Purpose: Custom crawling solutions for unique data extraction or indexing tasks.
They require coding knowledge but give you full control over what, how, and where to crawl.
No-code or low-code tools that let non-programmers extract data from websites using visual point-and-click interfaces.
Examples: Octoparse, ParseHub
Purpose: Ideal for marketers, researchers, or analysts who need data without writing a line of code.
let’s tackle the big question: how do crawlers work?
Here’s a simplified version of what happens behind the scenes:
Understanding how do web crawlers work helps you build a site that search engines like and that ranks as well.
Website crawling isn’t just a technical process it’s one of the pillars of SEO.
Lets discuss why:
If you’re wondering how to improve your website crawling and indexing, follow these best practices:
7. Tools to Monitor Website Crawling
Here are some of my go-to tools:
These tools are essential for managing and improving how your site interacts with any search engine web crawler.
In SEO, understanding what is website crawling and how web crawlers work isn’t optional it’s essential. Whether you’re fixing indexing issues, optimizing for faster crawling, or choosing the right audit tools, a strong foundation in crawling knowledge sets you up for long-term search success. And remember when it comes to URL crawl strategy, small changes can lead to big wins.