SHA Hash Generator: What It Is, How It Works & Why It Matters
- June 17, 2025
- 0

In the digital era, data security is more than a necessity it’s a priority. Tools like SHA hash generators play a critical role. Whether verifying file integrity, handling sensitive data, or building secure applications, SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) is at the heart of modern hashing practices.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything one needs to know about SHA hash generators in a simple, even if you’re not a developer.
A SHA hash generator is a tool both online or built-in to programming languages that takes input like a password, file, or text and converts it into a fixed-length string of characters using the SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm). It’s a one-way function, meaning once the input is hashed, one can’t reverse it back to the original.
It is used for:
It is a digital fingerprint. No matter the input size, the output (hash) will always look the same in length but it’s completely unique and complex.
SHA works using a mathematical process that turns input data into a fixed-length hash. It doesn’t encrypt or hide data but simply represents data uniquely.
Here’s how it works in simple steps:
The beauty of SHA is?
A tiny change in input drastically changes the hash. For example:
makefile
CopyEdit
Input: hello
SHA-256: 2cf24dba5fb0a30e26e83b2ac5b9e29e1b161e5c1fa7425e73043362938b9824
Change “hello” to “Hello” and the hash is completely different.
There are several types of SHA algorithms under the Secure Hash Standard (SHS), each with different levels of strength:
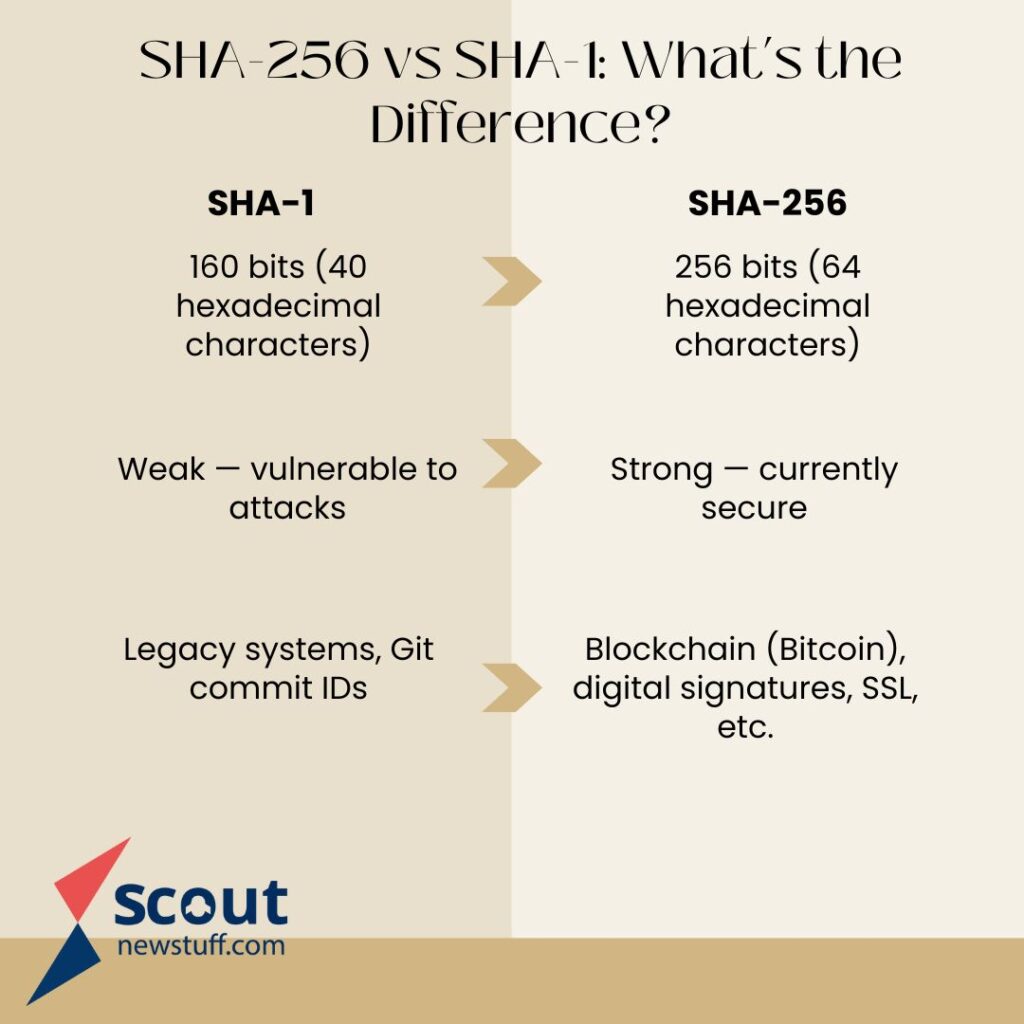
| Feature | SHA-1 | SHA-256 |
| Full Name | Secure Hash Algorithm 1 | Secure Hash Algorithm 256 |
| Hash Length | 160 bits (40 hexadecimal characters) | 256 bits (64 hexadecimal characters) |
| Security | Weak — vulnerable to attacks | Strong — currently secure |
| Speed | Faster (but less secure) | Slower (due to higher complexity) |
| Use Cases Today | Mostly deprecated | Widely used in modern applications |
| Released By | NSA in 1995 | NSA in 2001 (part of SHA-2 family) |
| Common Uses | Legacy systems, Git commit IDs | Blockchain (Bitcoin), digital signatures, SSL, etc. |
| Collision Resistance | Poor (collisions proven in 2017) | High (no known practical collisions) |
SHA especially SHA-256 is used to hash passwords before storing them in databases. But for more security, it’s better to use hashing algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2 because they’re slower and include salting.
When downloading files online, SHA hashes are often provided. One can re-generate the SHA hash locally and compare. If they match, the file is untouched.
Used in SSL certificates and digital documents to verify the authenticity and content integrity.
Every block in the blockchain has a SHA-256 hash that secures the data and links it to the next block.
You can use various online SHA hash generators for quick hashing. Some trusted ones include:
Simple to use:
Just paste the data → choose the algorithm → get the hash.
Note:
Don’t hash sensitive data online. Use local tools or programming functions for secure environments.
For techies and developers, command-line tools are efficient:
bash
CopyEdit
echo -n “yourdata” | shasum -a 256
powershell
CopyEdit
Get-FileHash -Algorithm SHA256 “file.txt”
python
CopyEdit
import hashlib
hashlib.sha256(b’hello’).hexdigest()
javascript
CopyEdit
crypto.subtle.digest(‘SHA-256’, new TextEncoder().encode(‘hello’))
php
CopyEdit
hash(‘sha256’, ‘hello’);
These are safer than using third-party services when handling passwords or user data.
SHA is perfect for data integrity, signatures, and blockchain, but not strong enough for modern password security. If you’re storing passwords then SHA alone is not enough because:
For password hashing, it’s better to prefer:
SHA hash generators are powerful tools that help to ensure data hasn’t been tampered with. They’re fast, reliable, and critical in cybersecurity, but knowing their limits is just as important. If you’re serious about data protection whether you’re a developer, system admin, or everyday user understanding how SHA works puts you ahead in the game.